Introduction
If you’ve spent any time in the gym or fitness world, you’ve heard the debate: cutting vs bulking. Should you eat more to build muscle, or eat less to get lean? Why do some people bulk and gain too much fat, while others cut and lose muscle?
The truth is simple:
Cutting and bulking are tools — not lifestyles.
When used correctly, they help sculpt your physique efficiently. When used incorrectly, they stall progress, wreck hormones, and kill motivation.
This definitive guide breaks down exactly what cutting and bulking are, how they work, their pros and cons, common mistakes, and how to choose the right phase for your goals.
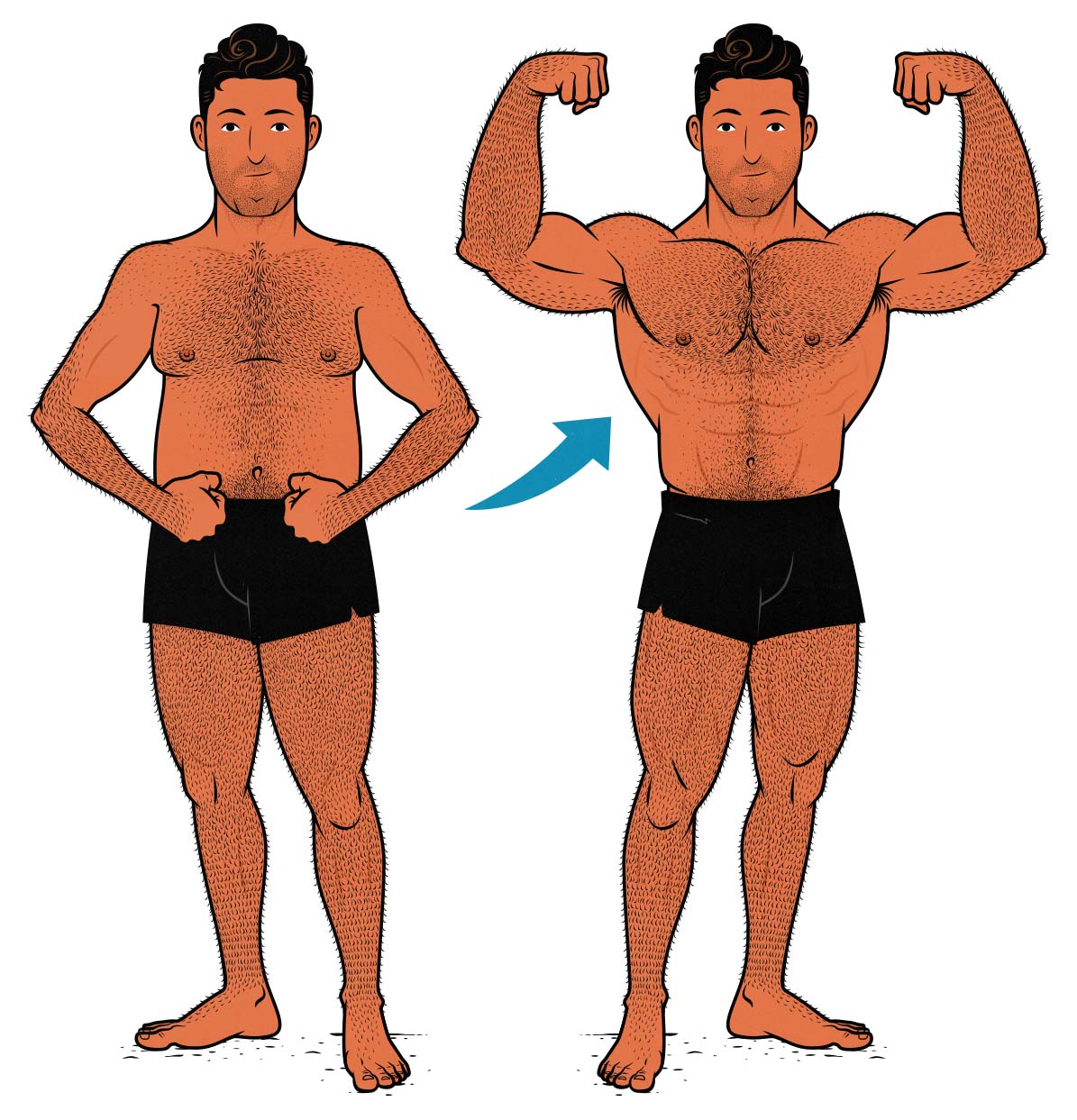
What Is Bulking?
Bulking is a structured phase where you consume more calories than your body burns to promote muscle growth.
The Goal of Bulking
- Increase muscle mass
- Improve strength
- Enhance training performance
- Support recovery
Muscle growth requires energy. Without a calorie surplus, building new muscle tissue becomes extremely difficult.
Types of Bulking
1. Clean Bulk
A clean bulk focuses on:
- Small calorie surplus (200–400 calories)
- Lean protein sources
- Complex carbohydrates
- Healthy fats
Pros:
- Minimal fat gain
- Easier cutting phase later
- Better health and digestion
Cons:
- Slower muscle gain
- Requires discipline
2. Dirty Bulk
A dirty bulk involves:
- Large calorie surplus
- Less concern for food quality
- Fast weight gain
Pros:
- Rapid strength gains
- Easier calorie intake
Cons:
- Excess fat gain
- Longer, harder cutting phase
- Poor health markers
👉 For most people, clean bulking is superior.
How to Bulk Properly
To bulk effectively:
- Eat 250–500 calories above maintenance
- Protein intake: 1.6–2.2g per kg of bodyweight
- Prioritize progressive overload
- Train with volume and intensity
- Sleep 7–9 hours nightly
- Monitor fat gain weekly
Good bulking foods include:
- Lean meats
- Eggs
- Rice, potatoes, oats
- Fruits and vegetables
- Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts)

What Is Cutting?
Cutting is a phase where you eat fewer calories than your body burns to reduce body fat while preserving muscle mass.
The Goal of Cutting
- Lose body fat
- Maintain muscle
- Improve definition and conditioning
- Enhance metabolic efficiency
Cutting is about fat loss, not weight loss.
How cutting phase bodybuilding Works
When calories are reduced:
- The body uses stored fat for energy
- Muscle loss becomes a risk if protein and training are inadequate
A successful cut balances:
- Calorie deficit
- High protein intake
- Resistance training
- Proper recovery
How to Cut Fat Without Losing Muscle
This is where most people fail.
Key Cutting Principles
- Moderate calorie deficit (300–500 calories)
- High protein intake
- Continue lifting heavy
- Avoid excessive cardio
- Manage stress and sleep
Protein Is Non-Negotiable
Aim for:
- 2.0–2.4g protein per kg of bodyweight
Cutting Diet vs Bulking Diet
| Aspect | Bulking | Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Surplus | Deficit |
| Goal | Build muscle | Lose fat |
| Protein | Moderate–High | High |
| Carbs | High | Moderate |
| Fats | Moderate | Moderate |
| Training | High volume | High intensity |
| Cardio | Minimal | Strategic |
Cutting vs Bulking: Key Differences
Bulking phase bodybuilding Pros
- Faster muscle growth
- Increased strength
- Better recovery
- Higher energy levels
Bulking Cons
- Fat gain
- Requires later cutting
Cutting Pros
- Leaner physique
- Improved definition
- Better insulin sensitivity
Cutting Cons
- Reduced energy
- Slower recovery
- Muscle loss risk if done incorrectly
Body Recomposition: An Alternative Approach
Body recomposition aims to:
- Build muscle
- Lose fat
- At the same time
It works best for:
- Beginners
- People returning after a break
- Those with higher body fat
However, recomposition is slower than traditional bulking or cutting.
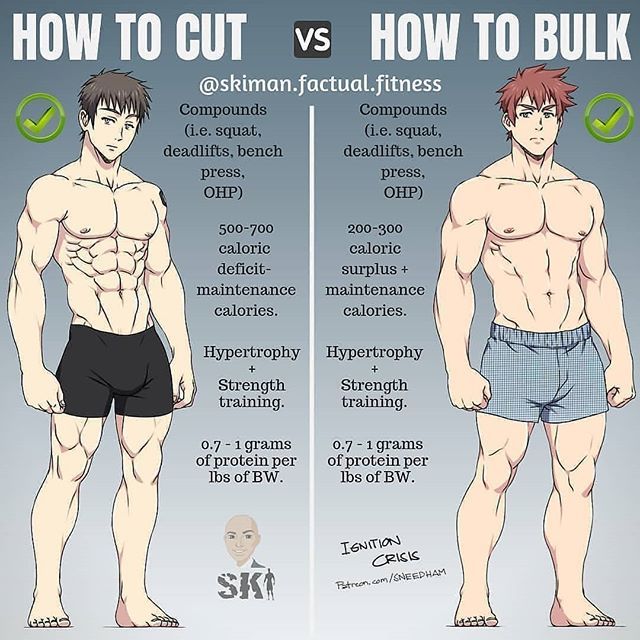
Which Should You Choose: Cutting or Bulking?
Choose Bulking If:
- You are lean (under ~12–15% body fat)
- Strength gains are the priority
- You struggle to gain muscle
Choose Cutting If:
- Body fat is above ~18–20%
- You want visible abs and definition
- Health and conditioning matter
Not Sure?
Start with a short cut, then transition into a clean bulk.
Common Cutting & Bulking Mistakes
Bulking Mistakes
- Eating too much junk
- Gaining fat too fast
- Neglecting cardio completely
- Ignoring digestion and health
Cutting Mistakes
- Slashing calories too aggressively
- Overdoing cardio
- Not lifting heavy
- Under-eating protein
Training During Cutting vs Bulking
Bulking Training
- Higher volume
- More sets per muscle
- Focus on progressive overload
Cutting Training
- Maintain strength
- Lower volume slightly
- Keep intensity high
Supplements That Support Cutting & Bulking
While supplements don’t replace diet:
For Bulking
- Protein powder
- Creatine
- Digestive enzymes
For Cutting
- Fat burners (thermogenics)
- Caffeine
- Electrolytes
How Long Should You Bulk or Cut?
- Bulking: 8–20 weeks
- Cutting: 6–12 weeks
Avoid staying in a deficit too long — hormones and metabolism suffer.
Final Verdict: Cutting vs Bulking
There is no “better” option — only the right phase at the right time.
- Bulk to build muscle
- Cut to reveal muscle
- Cycle intelligently
- Prioritize health, sleep, and recovery
Master both phases, and you’ll unlock consistent, long-term physique progress.


[…] guide breaks down the real science behind thermogenesis, how it affects fat burning, the different types of thermogenesis, and how you can naturally […]
Hi, kam dashur të di çmimin tuaj
Përshëndetje, ju lutem merrni një moment të shkurtër dhe shfletoni produktet tona, faleminderit.