Introduction: what is thermogenesis?
Fat loss is one of the most misunderstood topics in fitness. While many people focus only on calories, workouts, or supplements, the real driver behind fat burning lies deeper — in a physiological process called thermogenesis.
Thermogenesis is the reason your body burns calories at rest, heats itself, and converts food into usable energy. Understanding how thermogenesis works gives you a massive advantage when it comes to losing fat efficiently, sustainably, and intelligently.
This guide breaks down the real science behind thermogenesis, how it affects fat burning, the different types of thermogenesis, and how you can naturally optimize it.
What Is Thermogenesis?
Thermogenesis is the process by which the body produces heat by burning calories.
Every time your body:
- digests food
- moves muscles
- regulates temperature
- maintains organ function
…it produces heat. That heat comes from energy expenditure, which is directly linked to fat loss.
In simple terms:
👉 More thermogenesis = more calories burned
Why Thermogenesis Matters for Fat Loss
Fat loss occurs when your body burns more calories than it consumes. Thermogenesis controls:
- how many calories you burn at rest
- how efficiently food is processed
- how active your metabolism remains
If thermogenesis slows down, fat loss becomes harder — even with strict dieting.
This is why two people eating the same calories can experience very different results.
The Science Behind thermogenesis fat burning
Before diving deeper into thermogenesis, it’s important to understand how fat is actually burned.
How Fat Loss Works: ways to increase thermogenesis
- Calories are consumed through food
- Excess energy is stored as fat
- When energy demand increases, stored fat is released
- Fatty acids are transported to cells
- Fat is oxidized and used for energy
- Heat is produced — this is thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is the final step in fat burning.
The 4 Main Types of Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is not one single process. It occurs through multiple mechanisms.
1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
BMR represents the calories your body burns at rest just to stay alive.
It includes:
- breathing
- heart function
- brain activity
- hormone regulation
BMR accounts for 60–70% of daily calorie expenditure.
Factors Affecting BMR
- Muscle mass
- Age
- Genetics
- Hormones
- Body size
More muscle = higher BMR = increased thermogenesis.
2. Diet-Induced Thermogenesis (DIT)
Also called the thermic effect of food, DIT refers to the calories burned during digestion, absorption, and metabolism of nutrients.
Thermic Effect by Macronutrient
- Protein: 20–30%
- Carbohydrates: 5–10%
- Fats: 0–3%
Protein has the highest thermogenic effect, making it critical for fat loss diets.
👉 This is why high-protein diets support fat burning even at equal calories.
3. Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)
NEAT includes all movement that is not formal exercise:
- walking
- standing
- fidgeting
- posture adjustments
- daily tasks
NEAT can vary by hundreds of calories per day between individuals.
Why NEAT Is So Important
During calorie restriction, the body often subconsciously reduces movement — lowering thermogenesis and slowing fat loss.
Maintaining NEAT prevents metabolic slowdown.
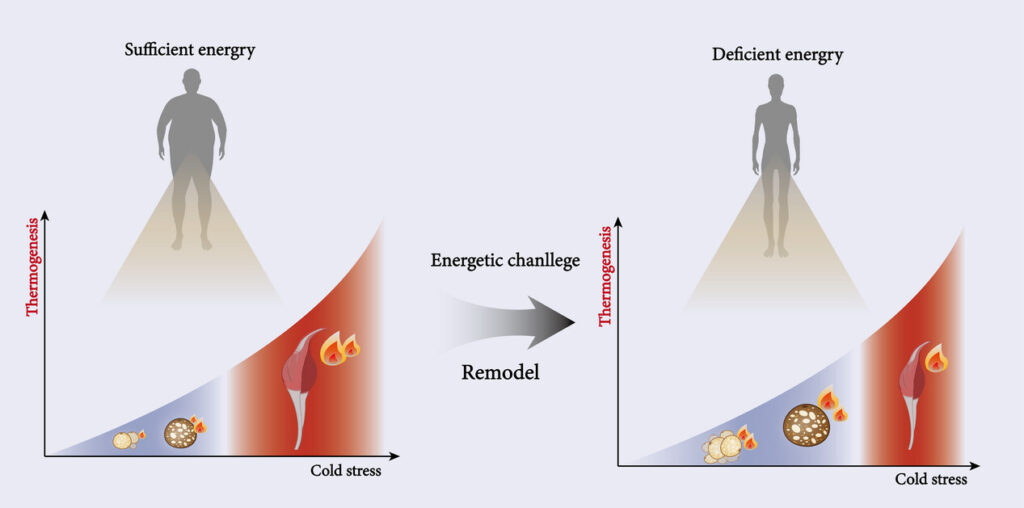
4. Adaptive Thermogenesis
Adaptive thermogenesis is the body’s survival mechanism.
When calories drop too low:
- metabolism slows
- heat production decreases
- energy expenditure drops
This is why aggressive dieting often leads to plateaus.
Signs of Adaptive Thermogenesis
- Feeling cold
- Fatigue
- Reduced strength
- Low motivation
- Slower fat loss
Understanding this process is key to sustainable dieting.
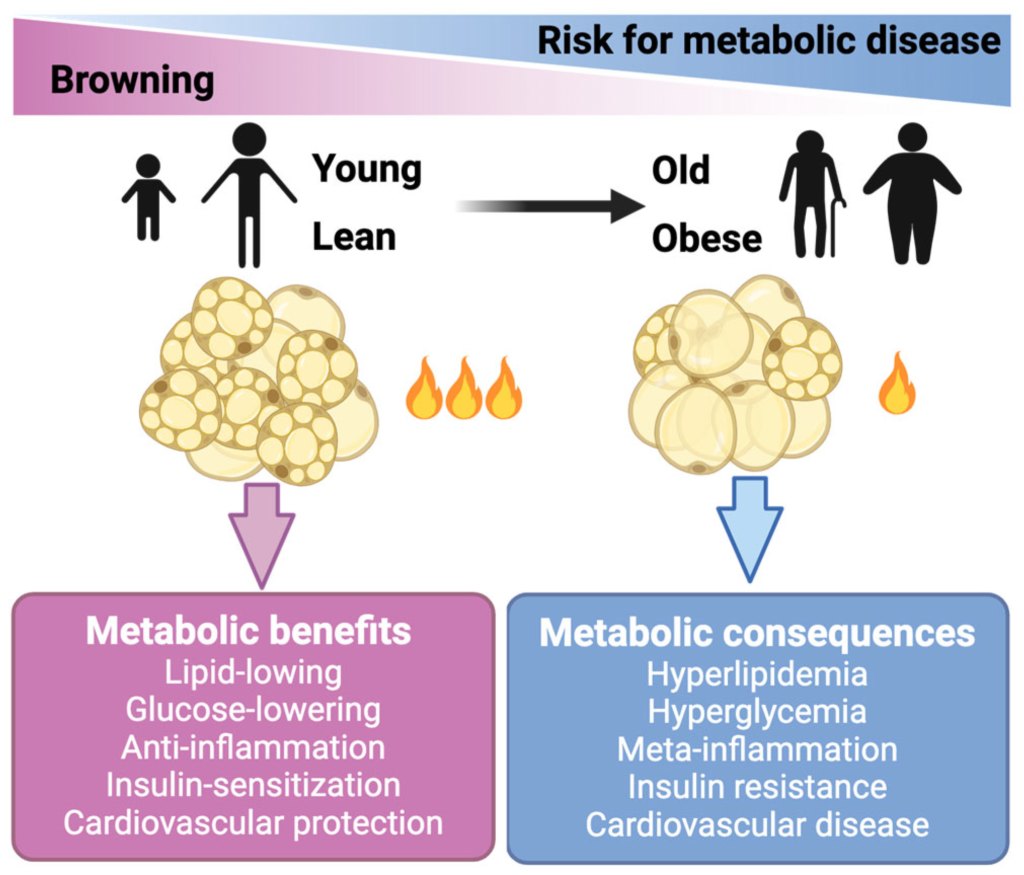
Brown Fat and Thermogenesis
Unlike white fat (which stores energy), brown adipose tissue (BAT) burns calories to produce heat.
Brown fat:
- contains high mitochondrial density
- increases thermogenesis
- improves metabolic health
Cold exposure and certain nutrients may activate brown fat, increasing fat burning.
How Thermogenesis Affects Metabolism
Metabolism is not fixed. Thermogenesis fluctuates based on:
- food intake
- activity levels
- stress
- sleep
- hormones
A healthy metabolism is one that maintains thermogenesis even during fat loss phases.
Ways to Increase Thermogenesis Naturally
You don’t need extreme methods to boost thermogenesis. Small strategies compound over time.
1. Build Lean Muscle
Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat.
Resistance training directly increases basal thermogenesis.
2. Eat Enough Protein
Protein:
- increases diet-induced thermogenesis
- preserves muscle
- improves satiety
Aim for 1.6–2.4g per kg of bodyweight.
3. Stay Physically Active Outside the Gym
Walking more, standing desks, and daily movement all elevate NEAT.
4. Avoid Extreme Calorie Deficits
Moderate deficits preserve thermogenesis better than aggressive cuts.
5. Manage Stress and Sleep
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which suppresses thermogenesis and fat loss.
Thermogenesis vs Fat Burners: how thermogenesis works
Thermogenic supplements aim to:
- increase heat production
- elevate metabolic rate
- enhance fat oxidation
However, supplements should support — not replace — fundamentals like diet, training, and sleep.
Common Myths About Thermogenesis
Myth 1: Sweating Means Fat Loss
Sweat is water loss, not fat burning.
Myth 2: More Cardio Equals More Thermogenesis
Excessive cardio can lower adaptive thermogenesis over time.
Myth 3: Metabolism Is Permanent
Metabolism adapts — both positively and negatively.
thermogenesis fat burning
Sustainable fat loss depends on:
- preserving muscle
- maintaining NEAT
- supporting metabolic health
- cycling calories intelligently
Understanding thermogenesis prevents plateaus and rebound weight gain.
thermogenesis fat burning Explained Simply
To summarize:
- Thermogenesis = calorie burning through heat production
- It occurs through digestion, movement, and metabolic activity
- Higher thermogenesis = easier fat loss
- Poor dieting habits suppress thermogenesis
- Smart training and nutrition enhance it
Final Thoughts: Master the Science, Control the Results
Fat loss isn’t magic — it’s biology.
Thermogenesis is the foundation of fat burning, and understanding it allows you to work with your body instead of against it.
By supporting thermogenesis through intelligent nutrition, movement, recovery, and consistency, fat loss becomes predictable, sustainable, and far less frustrating.